Breathing Exercises for Pleural Effusion Patients

Breathing is an essential life process that we generally take for granted. However, for individuals with pleural effusion, a condition characterized by an abnormal buildup of fluid in the pleural space surrounding the lungs, breathing can become challenging and uncomfortable. If you or someone you know is struggling with pleural effusion (which often results from underlying conditions such as lung infections, cancer, heart disease, liver failure, and so on), then incorporating specific breathing exercises may help improve respiratory health and enhance overall well-being.
Pleural effusion often requires medical intervention to drain the fluid from the pleural space and treat the underlying condition causing the pleural effusions. However, certain breathing exercises can potentially aid in the restoration of lung function when afflicted by pleural effusion and provide relief for patients. Let’s explore some of these breathing exercises further.
The Importance of Breathing Exercises
Breathing exercises can offer numerous benefits to pleural effusion patients. First, they help maintain lung capacity and mitigate the exacerbation of breathing complications. Second, they can improve breathing efficiency by strengthening the respiratory muscles, promoting oxygenation, and enhancing overall lung function. Third, practicing breathing exercises can prevent the reduction of shortness of breath, anxiety, and stress often associated with pleural effusion.
Types of Breathing Exercises for Pleural Effusion Patients
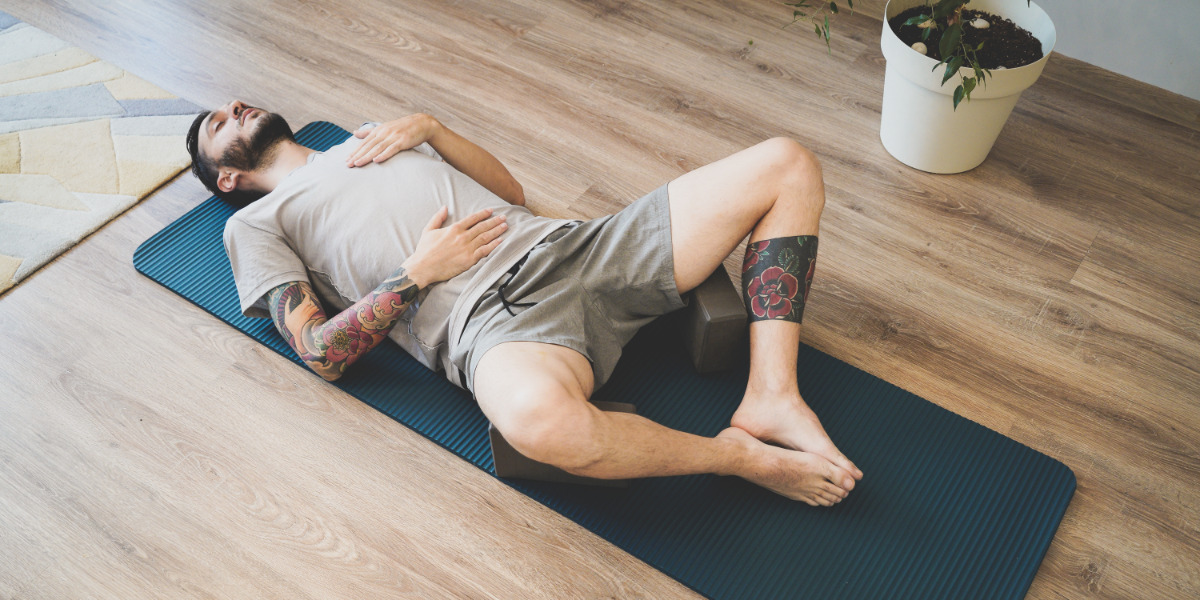
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: This exercise focuses on engaging and strengthening the diaphragm, the primary muscle responsible for inhalation. To perform diaphragmatic breathing, sit or lie down in a comfortable position, place one hand on your abdomen, and inhale deeply through your nose while expanding your abdomen. Exhale slowly through pursed lips, allowing your abdomen to contract naturally. Repeat this exercise for 5-10 minutes, gradually increasing the duration as your tolerance improves.
- Pursed Lip Breathing: Pursed lip breathing involves consciously controlling the exhalation phase of breathing. Begin by inhaling slowly through your nose, then pursing your lips as if you are about to blow out a candle. Exhale gently through your pursed lips for twice as long as your inhalation. This exercise helps to prolong exhalation, release trapped air, and maintain optimal oxygen levels in the lungs.
- Segmental Breathing: Pleural effusion may affect specific regions around the lungs. Segmental breathing exercises aim to target these affected areas using controlled breaths. Start by placing your hand on the affected area and inhaling slowly. Visualize sending your breath into the specific area, feeling it expand as you inhale. Exhale fully and gently. Repeat this exercise for each affected segment, focusing on one area at a time.
Additional Tips for Breathing Exercises
Incorporate the following tips to maximize the benefits of breathing exercises for pleural effusion patients:
- Practice breathing exercises in a relaxed environment, free from distractions.
- Remember to maintain good posture while performing the exercises to enhance lung capacity.
- Start with shorter durations and gradually increase the time as your tolerance and lung function improve.
- Seek guidance and supervision from a healthcare professional or certified respiratory therapist to ensure proper technique.
The incorporation of breathing exercises into your routine can greatly benefit pleural effusion patients by improving lung capacity, maintaining respiratory function, and reducing discomfort. Ask your doctor if practicing diaphragmatic breathing, pursed lip breathing, and segmental breathing exercises is right for you. If you need help with the best exercises for your specific lung condition, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
At Prana Pulmonary Clinic, our team of experienced pulmonary healthcare experts is dedicated to helping pleural effusion patients navigate, diagnose, and treat their respiratory challenges. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you improve your respiratory health.